Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): systems that perform tasks that normally require human intelligence (problem solving, perception, language, planning).
- Machine Learning (ML): a subfield of AI where models learn patterns from data.
- Deep Learning (DL): ML using multi-layer neural networks (high-capacity, representation learning). Textbook-level coverage of DL fundamentals and backpropagation are standard (Goodfellow et al.).
Classifications (high-level)
By approach
- Symbolic / Rule-based AI (logic, knowledge bases)
- Statistical / Probabilistic AI (Bayesian methods, probabilistic graphical models)
- Connectionist (Neural) (neural networks, deep learning)
By learning paradigm
- Supervised learning — labeled data (classification, regression).
- Unsupervised learning — no labels (clustering, representation learning, density estimation).
- Semi-supervised learning — mix of labeled + unlabeled.
- Self-supervised learning — tasks built from inputs themselves (contrastive, masked-prediction).
- Reinforcement learning (RL) — learning via rewards and environment interaction.
General tasks / application areas
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): language modeling, translation, Q&A, summarization, sentiment, token classification. (Transformers are dominant.)
- Computer Vision (CV): classification, detection (object detection), segmentation (semantic/instance), image generation (GANs, diffusion).
- Speech / Audio: ASR (speech-to-text), TTS (text-to-speech), speaker identification.
- Reinforcement Learning / Control: games, robotics, planning.
- Recommendation & Search: ranking, retrieval, embeddings.
- Generative modeling: GANs, VAEs, diffusion models (image/audio/text generation).
What is a neuron? (mathematics + named activation functions)
A single neuron (in feedforward networks) computes a weighted sum of its inputs, applies a bias, then passes that through an activation function.
Let input vector
Common activation functions (with equations):
Linear (identity):
. Sigmoid (logistic):
. Useful for binary probabilities; saturates for large |z|. 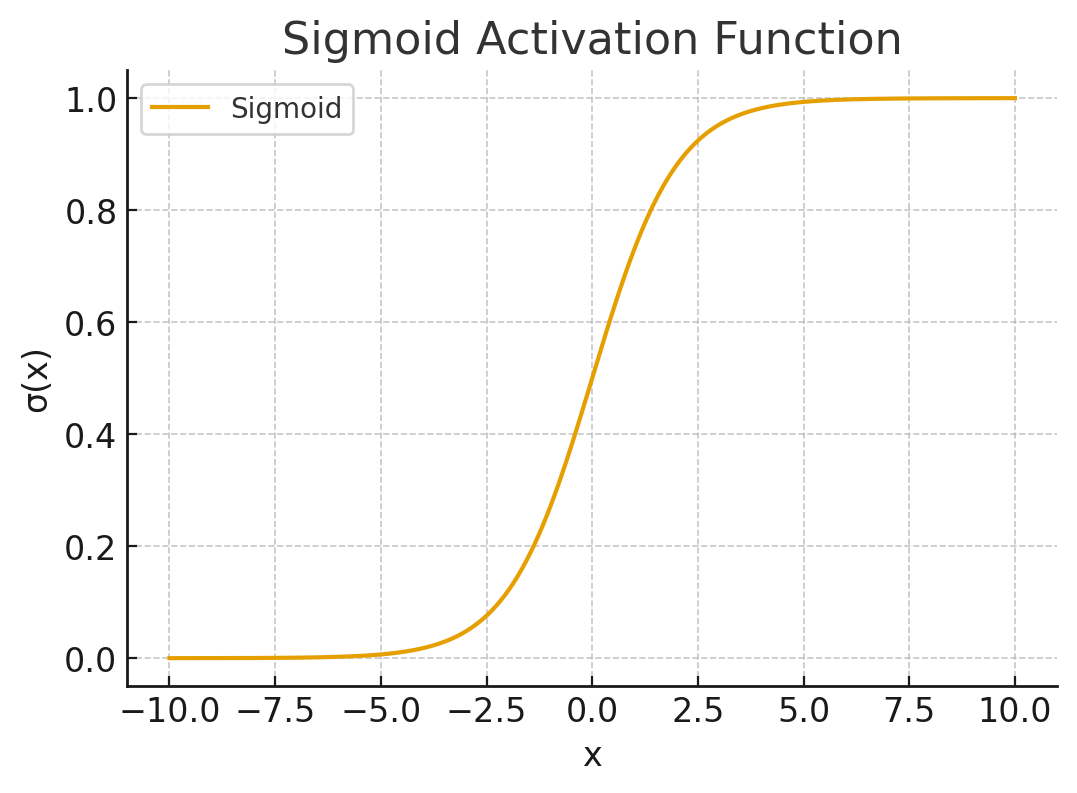
Tanh:
, ranges . 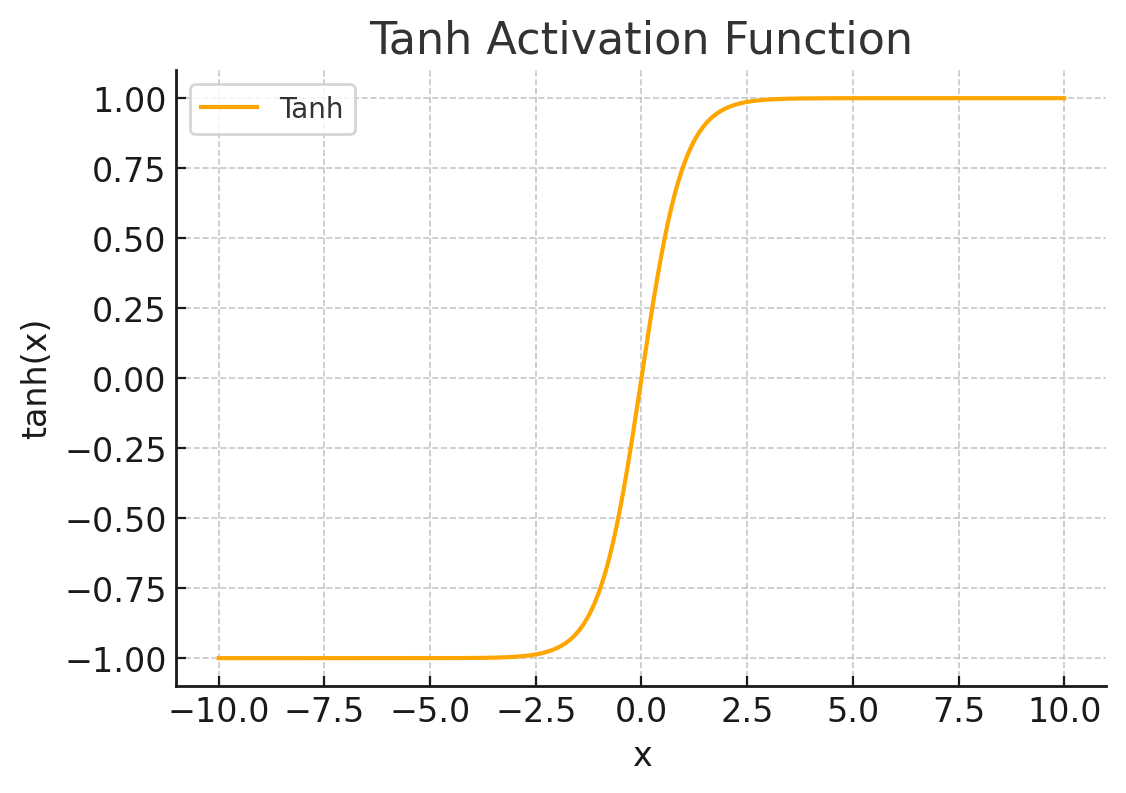
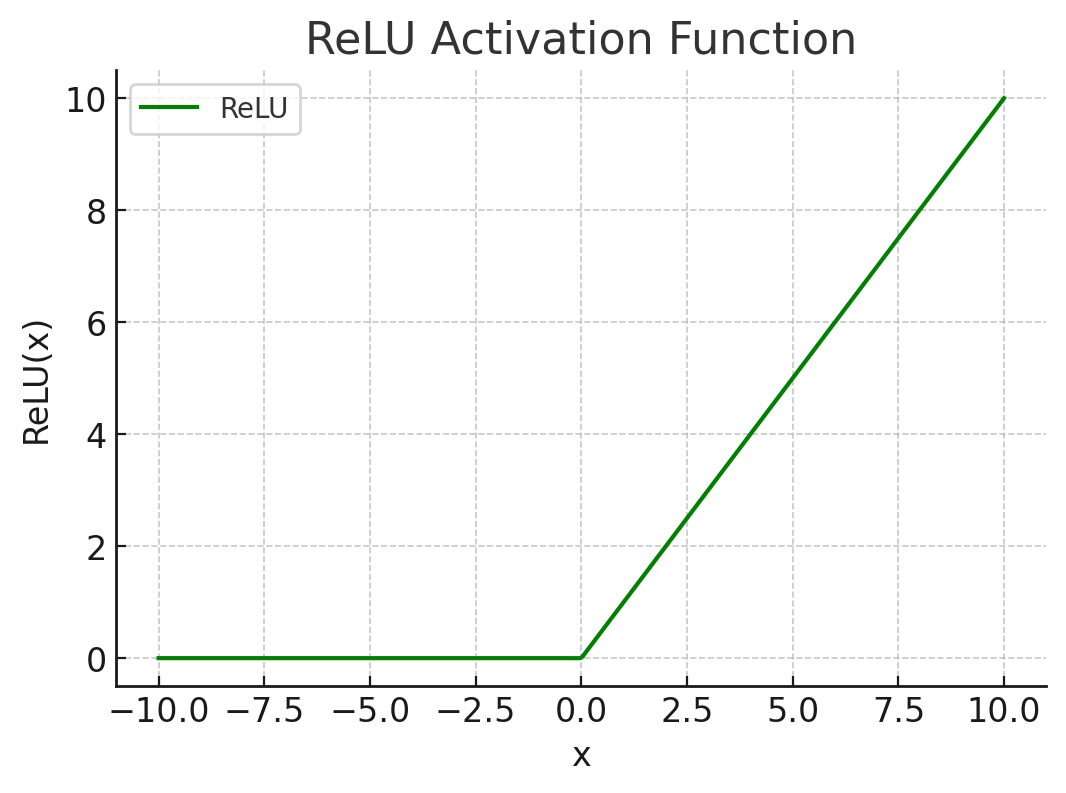
ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit):
. 
Leaky ReLU:
(small ). 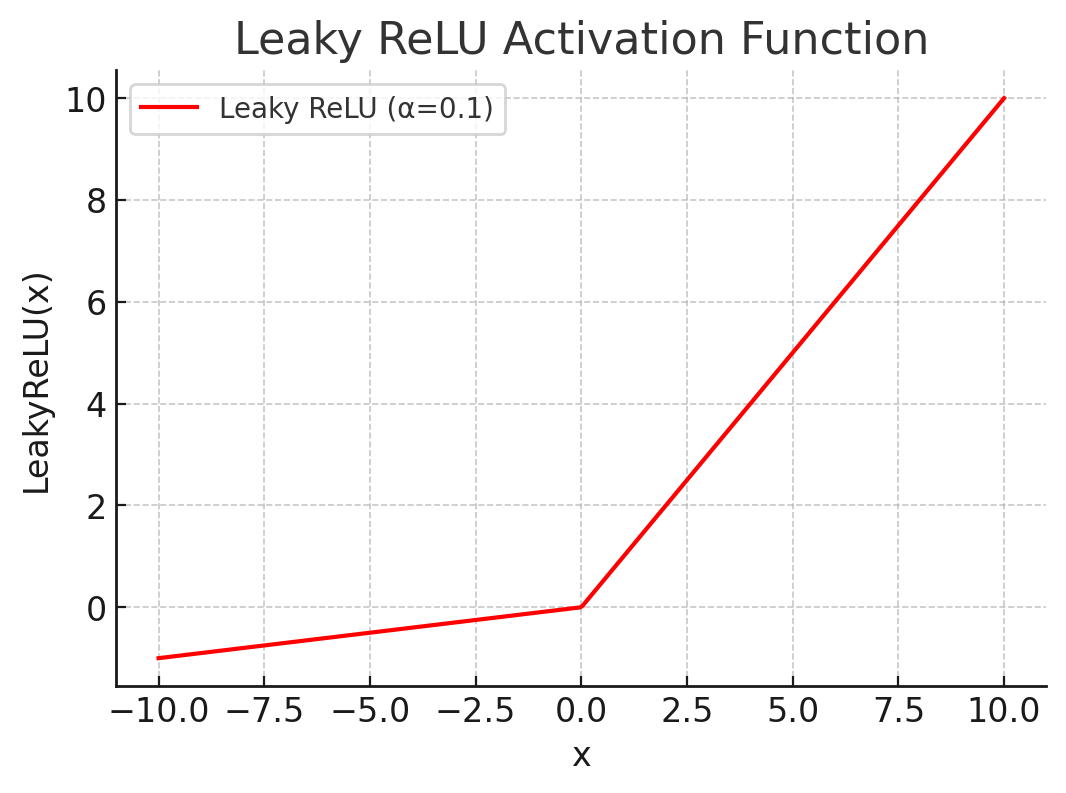
Softmax (multi-class output): for logits
, 
Softmax converts arbitrary logits into a probability distribution.
Loss Functions (a.k.a. Cost / Objective functions)
A loss function is a mathematical measure of how well (or poorly) a machine learning model is performing on a given task.
- It quantifies the difference between the model’s prediction (
) and the true target value ( ). - During training, the model adjusts its parameters (
) to minimize the loss. - The “optimization” process (via gradient descent or Adam, etc.) relies on the loss to compute parameter updates.
1. Why are they important?
- Define what “good performance” means for the task.
- Guide the optimization process (the gradients come from the loss).
- Different tasks need different loss functions (classification ≠ regression ≠ generative).
2. Common Loss Functions (with equations)
Regression Losses
Mean Squared Error (MSE)
Penalizes large errors more (quadratic).
Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
More robust to outliers than MSE.
Classification Losses
Binary Cross-Entropy (Log Loss) For binary labels
and predicted probability : Categorical Cross-Entropy (for multi-class, with one-hot targets
): Works together with Softmax to model probabilities.
Hinge Loss (used in SVMs):
Encourages correct classification with a margin.
Probabilistic & Generative Losses
Kullback–Leibler (KL) Divergence Measures difference between two probability distributions
and : (Used in Variational Autoencoders, language modeling, etc.)
Wasserstein Loss (Wasserstein distance, used in WGANs): Provides a smoother distance metric between real and generated distributions.
Negative Log-Likelihood (NLL)
A general loss form (e.g., for probabilistic models).
Reinforcement Learning Losses
Policy Gradient Loss (REINFORCE):
(Optimizes expected reward).
Temporal Difference (TD) Loss (for value functions):
3. Choosing the Right Loss
- Regression → MSE / MAE.
- Classification → Cross-entropy.
- Generative modeling → KL, Wasserstein, NLL.
- Reinforcement learning → Policy gradient / TD error.
Backpropagation & optimization — core equations
Gradient descent (batch):
where
Stochastic Gradient Descent (per mini-batch) uses same update but gradient estimated on batch.
Backpropagation: use chain rule to compute
where
Adam optimizer (named algorithm, Kingma & Ba) — key equations per iteration
This is one of the most widely used adaptive optimizers.
(Also know: SGD + momentum, RMSProp, etc.)
Major types of neural networks (what they are, when used)
MLP / Feedforward (Fully-connected): dense layers, universal function approximator (small/structured data).
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): local receptive fields, weight sharing — great for images, 2D signals (classification, detection, segmentation).
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): sequence models (suffer from vanishing gradients).
- LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) and GRU: gating mechanisms to preserve/forget information across long sequences (Hochreiter & Schmidhuber for LSTM).
Transformer: uses self-attention; highly parallelizable and state-of-the-art in NLP and many other domains. Key attention formula (scaled dot-product attention):
where
are query/key/value matrices and is key dimension. Transformers replaced recurrence in many sequence tasks. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs): operate on graphs (node/edge features, message passing).
Autoencoders (AE) and Variational AE (VAE): unsupervised representation learning; VAEs are probabilistic generative models.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): generator & discriminator in adversarial training (Goodfellow et al.).
Diffusion Models: denoise-from-noise generative models (recently became state-of-the-art for high-quality image generation). (See Ho et al., Sohl-Dickstein et al.)
Model creation / training workflow (practical steps & best practices)
Define objective & collect data
- Labeling strategy, dataset splits (train / val / test), distribution checks.
Data preprocessing & augmentation
- Normalize/standardize inputs, tokenization for text, image augmentations (flip, crop), audio feature extraction.
Model architecture selection
- Start small (baseline), increase capacity as needed. Consider transfer learning (pretrained backbones).
Loss function & metrics
- Choose loss matching task (CE for classification, MSE for regression). Decide metrics (accuracy, precision/recall/F1, AUC, BLEU, perplexity).
Optimizer & learning-rate schedule
- Choose optimizer (Adam common); use LR schedules (step, cosine, warmup). Learning-rate is often the most sensitive hyperparameter.
Regularization
- Weight decay (L2), dropout, early stopping, data augmentation, batch norm.
Monitoring & validation
- Track train/val loss/metrics. Use held-out test set only for final evaluation.
Hyperparameter tuning
- Grid search / random search / Bayesian (Optuna), and practical budgets. Use cross-validation if dataset small.
Model compression & deployment
- Quantization, pruning, distillation, converting to inference format (ONNX, TorchScript, TFLite, Core ML). See section 10.
Important evaluation metrics (named)
Accuracy:
(not reliable for imbalanced sets). Precision / Recall / F1:
ROC AUC: area under ROC curve (sensitivity vs 1-specificity).
BLEU (NLP translation quality), ROUGE (summarization), Perplexity (language models).
mAP (mean Average Precision) for object detection.
Model formats & deployment (common formats, when to use them)
PyTorch checkpoint (.pt / .pth) — native PyTorch state_dict or full model. Can be exported to TorchScript for C++/mobile inference. (.pt and .pth are basically conventions; both used).
TensorFlow SavedModel — canonical TensorFlow serialized model (directory with
saved_model.pb+ variables); used for TF Serving and conversions.ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) — open graph format to move models between frameworks and runtimes (good for deployment and optimizations).
TFLite — TensorFlow Lite for mobile/embedded, supports post-training quantization and conversion from SavedModel. Quantization reduces model size/latency (8-bit, etc.).
Core ML — Apple’s format for iOS deployment.
OpenVINO, TensorRT — vendor/runtime specific optimizers for Intel/NVIDIA hardware.
Model compression techniques
- Quantization: reduce numeric precision (e.g. float32→int8). Can be post-training or quantization-aware training.
- Pruning: remove weights/filters with small contribution.
- Knowledge distillation: train a smaller “student” to match a large “teacher”.
- Operator fusion / graph optimizations (runtime dependent).
Short list of foundational / reference papers & docs (for further reading)
- “Attention Is All You Need” — Vaswani et al., 2017 (Transformer, attention equation).
- “Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization” — Kingma & Ba (2014/2015) (Adam equations).
- Deep Learning (Goodfellow, Bengio, Courville) — textbook (backpropagation, convnets, theory).
- ONNX specification & docs — for model interchange.
- TensorFlow SavedModel / TFLite docs — for TensorFlow model export & quantization.
Useful mathematical reminders / cheat-sheet (key equations collected)
- Neuron forward:
. - Softmax:
. - Cross-entropy (categorical):
. - Gradient descent update:
. - Adam:
with bias-corrected and . - Scaled dot-product attention:
Cross-check / “what I verified” (short)
I verified and drew from:
- Transformer (attention formula & claims about architecture) — Vaswani et al. (2017).
- Adam optimizer equations (Kingma & Ba).
- Softmax & cross-entropy standard forms.
- ONNX and TensorFlow SavedModel / TFLite docs for model format practices and quantization (deployment & compression).
Structure :
- Approaches to AI: Turing Test and Rational Agent Approaches; State Space Representation of Problems, Heuristic Search Techniques, Game Playing, Min-Max Search, Alpha Beta Cutoff Procedures.
- Knowledge Representation: Logic, Semantic Networks, Frames, Rules, Scripts, Conceptual Dependency and Ontologies; Expert Systems, Handling Uncertainty in Knowledge.
- Planning: Components of a Planning System, Linear and Non Linear Planning; Goal Stack Planning, Hierarchical Planning, STRIPS, Partial Order Planning.
- Natural Language Processing: Grammar and Language; Parsing Techniques, Semantic Analysis and Prgamatics.
- Multi Agent Systems: Agents and Objects; Agents and Expert Systems; Generic Structure of Multiagent System, Semantic Web, Agent Communication, Knowledge Sharing using Ontologies, Agent Development Tools.
- Fuzzy Sets: Notion of Fuzziness, Membership Functions, Fuzzification and Defuzzification; Operations on Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Functions and Linguistic Variables; Fuzzy Relations, Fuzzy Rules and Fuzzy Inference; Fuzzy Control System and Fuzzy Rule Based Systems.
- Genetic Algorithms (GA): Encoding Strategies, Genetic Operators, Fitness Functions and GA Cycle; Problem Solving using GA.
- Artificial Neural Networks (ANN): Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement Learning; Single Perceptron, Multi Layer Perceptron, Self Organizing Maps, Hopfield Network.
